Ensure consistent m/z axis
Background
A common method for reducing the size of the data without discarding information when saving mass spectrometry data is to only store data points where the intensity is greater than zero. This can result in the data points in any two spectra containing different m/z values (for example in one spectrum there may be a peak at 798.55 and therefore a corresponding data point, but in the next spectrum this peak was not detected and therefore this value is not present in the spectrum).
This method of storing spectra can cause issues for spectral visualisation, combining spectra (such as calculating an average, or generating a ‘data cube’) or performing preprocessing methods (such as smoothing or baseline correction).
- In the case of visualisation it is important that the zeros are replaced.
- In the case of combining spectra it is important that the spectra are consistent (i.e. that each spectrum has intensity values for exactly the same m/z values).
- In the case of preprocessing it is important that the m/z values are regularly distributed.
Applying a method in SpectralAnalysis
- Select a spectrum by clicking on a pixel in the image.
- Open
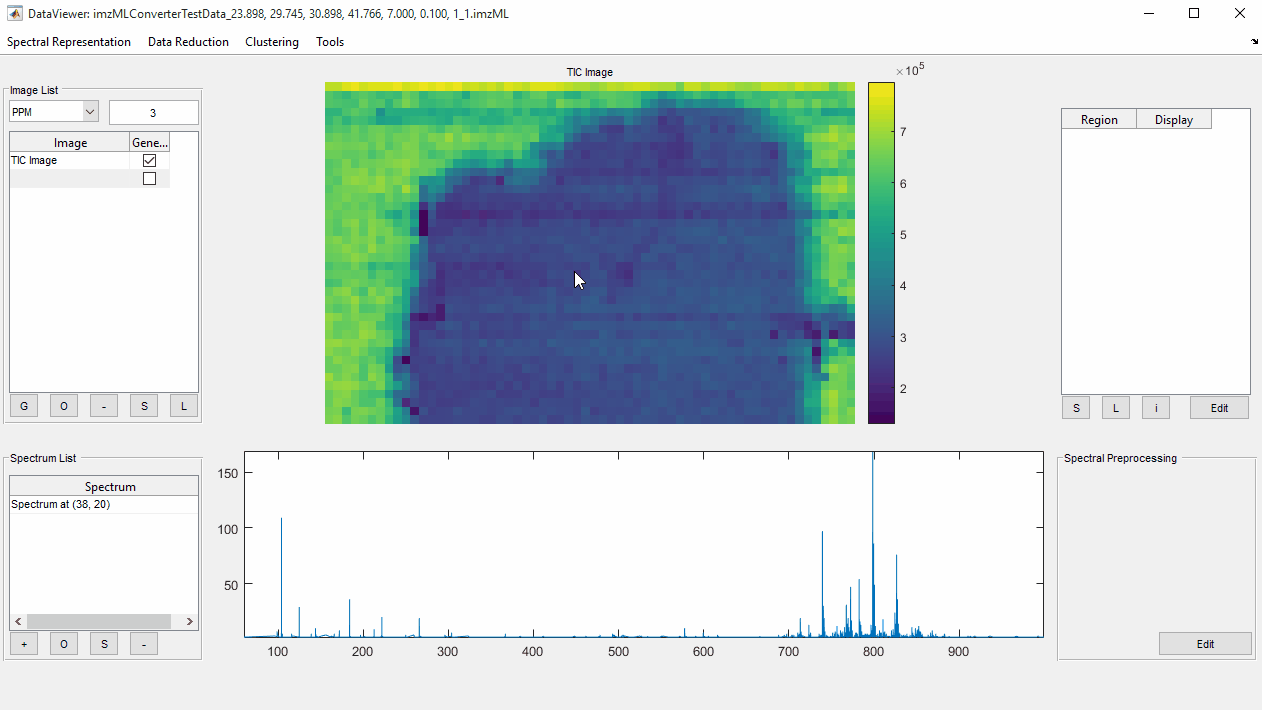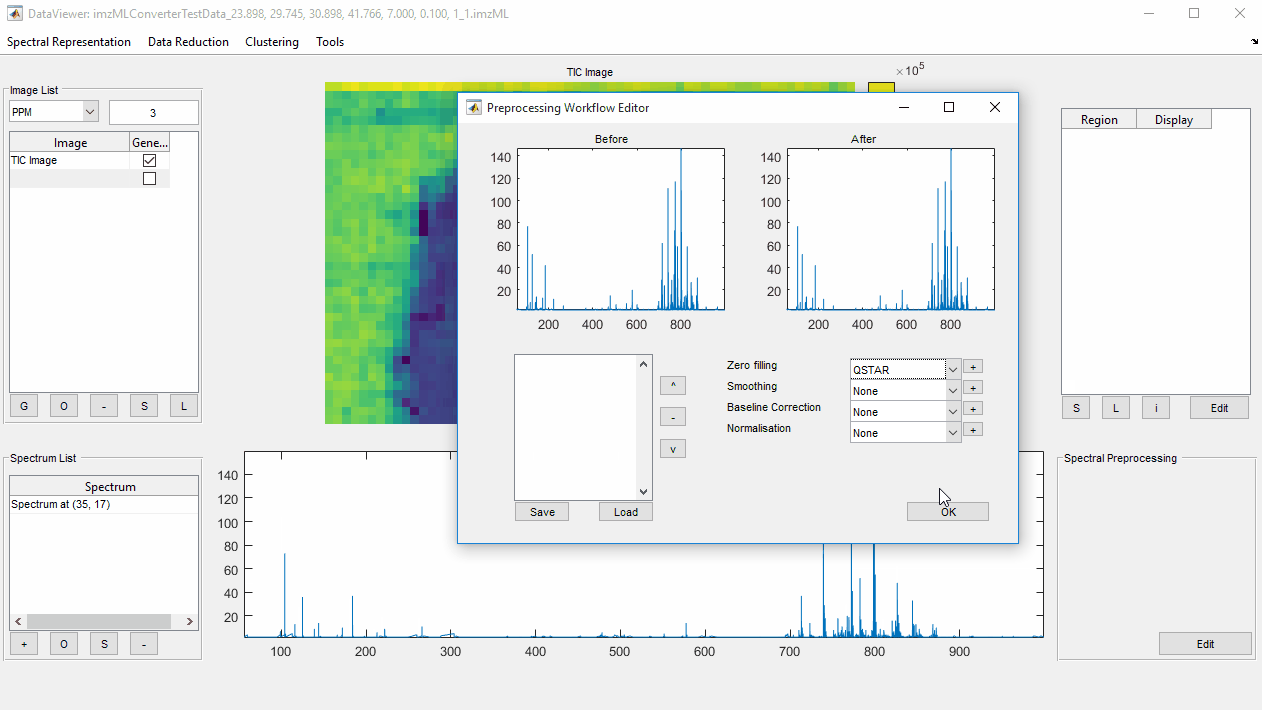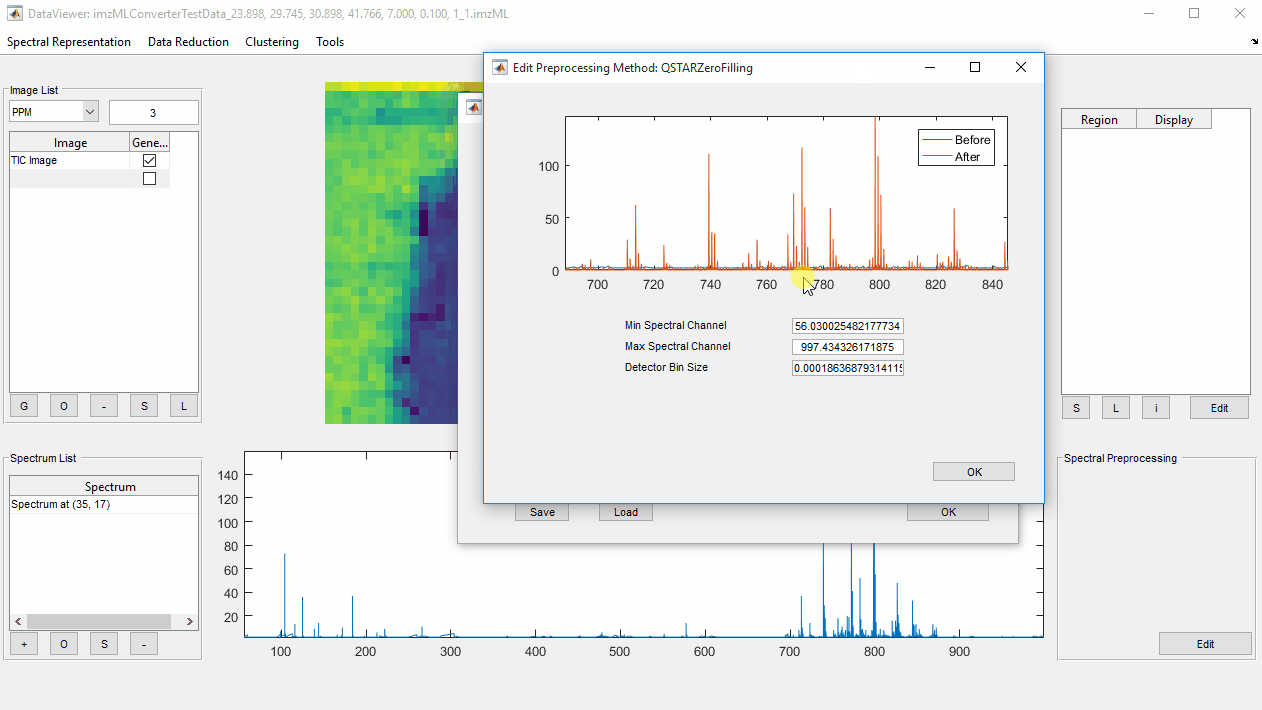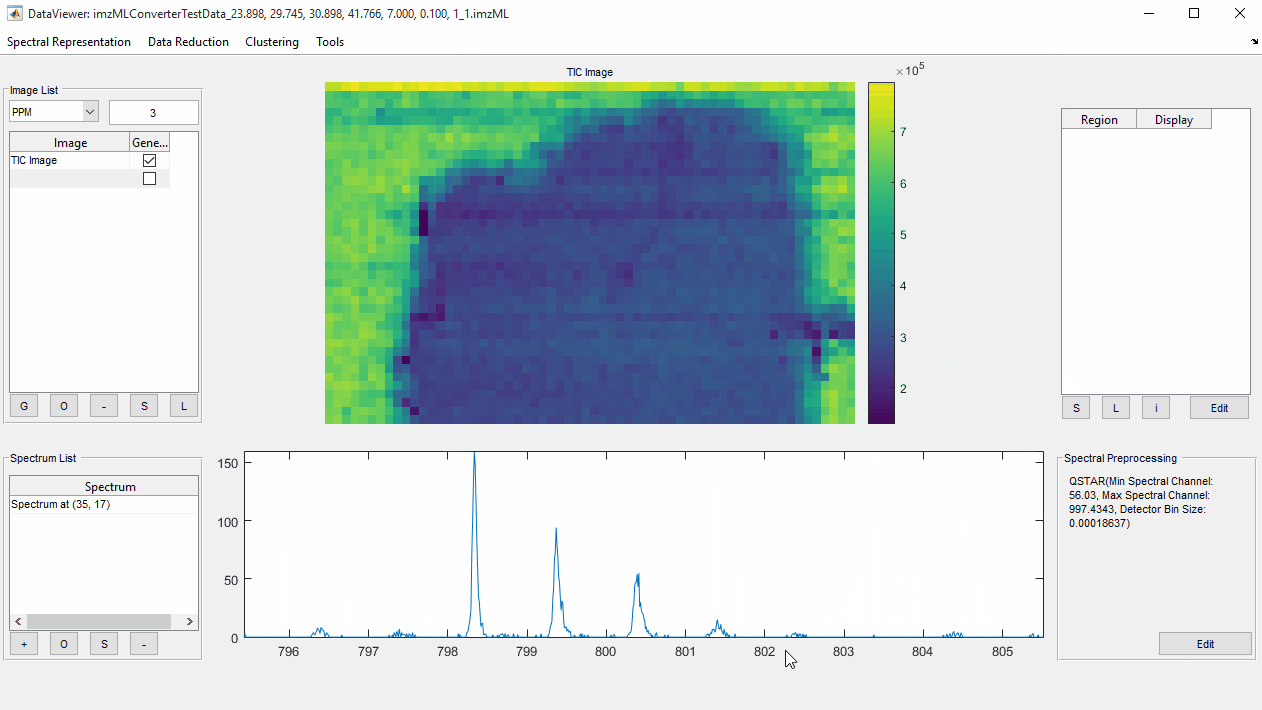
Preprocessing Workflow Editorby selectingEditbutton inSpectral Preprocessingpanel. - Select most appropriate
Zero Fillingmethod (see Choosing the most appropriate method section below) and click the adjacent+button. - Enter desired parameters for the chosen method (if appropriate, and applicable), optionally checking the effect of the zero filling method by zooming into the spectrum and observing the ‘before’ and ‘after’ spectra.
- Click
OKto close theEdit Preprocesing Methodwindow and thenOKagain to close thePreprocessing Workflow Editor. The chosen method(s) will now be automatically applied to any viewed spectrum.
Choosing the most appropriate method
The most appropriate method to use depends on the data and the desired next step in the processing workflow. The methods included in SpectralAnalysis are described below.
- Combine Bins
- Fixed Point per Peak Interpolation Rebin
- Interpolation PPM Rebin
- Interpolation Rebin
- Orbitrap
- QSTAR
- PPM Rebin
- Rebin
- Calibration
- Synapt
Rebin
Specify a m/z bin size, and a m/z range. The resulting m/z axis then spans the specified m/z range consisting of equally sized bins. All data points which fall within one of the bins are then added together to generate the resulting spectrum.
PPM Rebin
Specify a PPM bin size, and a m/z range. The resulting m/z axis then spans the specified m/z range consisting of bins of increasing size (each bin has a constant size in PPM, but as PPM is proportional to m/z, the bin size increases as m/z increases). All data points which fall within one of the bins are then added together to generate the resulting spectrum.
Interpolation Rebin
Specify a m/z bin size, and a m/z range. The resulting m/z axis then spans the specified m/z range consisting of equally sized bins. All data points are then interpolated onto the new m/z axis (linear interpolation).
Interpolation PPM Rebin
Specify a PPM bin size, and a m/z range. The resulting m/z axis then spans the specified m/z range consisting of bins of increasing size (each bin has a constant size in PPM, but as PPM is proportional to m/z, the bin size increases as m/z increases). All data points are then interpolated onto the new m/z axis (linear interpolation).